New Release: The Gorilla Guide To…® Enabling IT at the Edge, Express Edition!

When smart devices (mobile phones and tablets) became popular after 2010, there was a rush to the cloud to compensate for the limited memory and compute power on those devices. But they’ve gotten much powerful since their early years. They can even do face recognition without sending data to the cloud. And Internet of Things (IoT) devices are also becoming more powerful. Protocols such as Bluetooth Low Energy and Zigbee make data transfer over low-power devices more efficient.
Now the movement back to the edge is gathering stream. An “edge” doesn’t necessarily mean a tiny 16-bit device dribbling away precious battery power—it could be a fully operational data center at a remote retail outlet or cell tower. The key definition of the edge is that you’re doing a lot of compute processing and data storage right were the data is collected, while still controlling those systems from a central point. The payoff is much faster response to events. Figure 1 shows some modern applications that take advantage of IoT and edge computing.
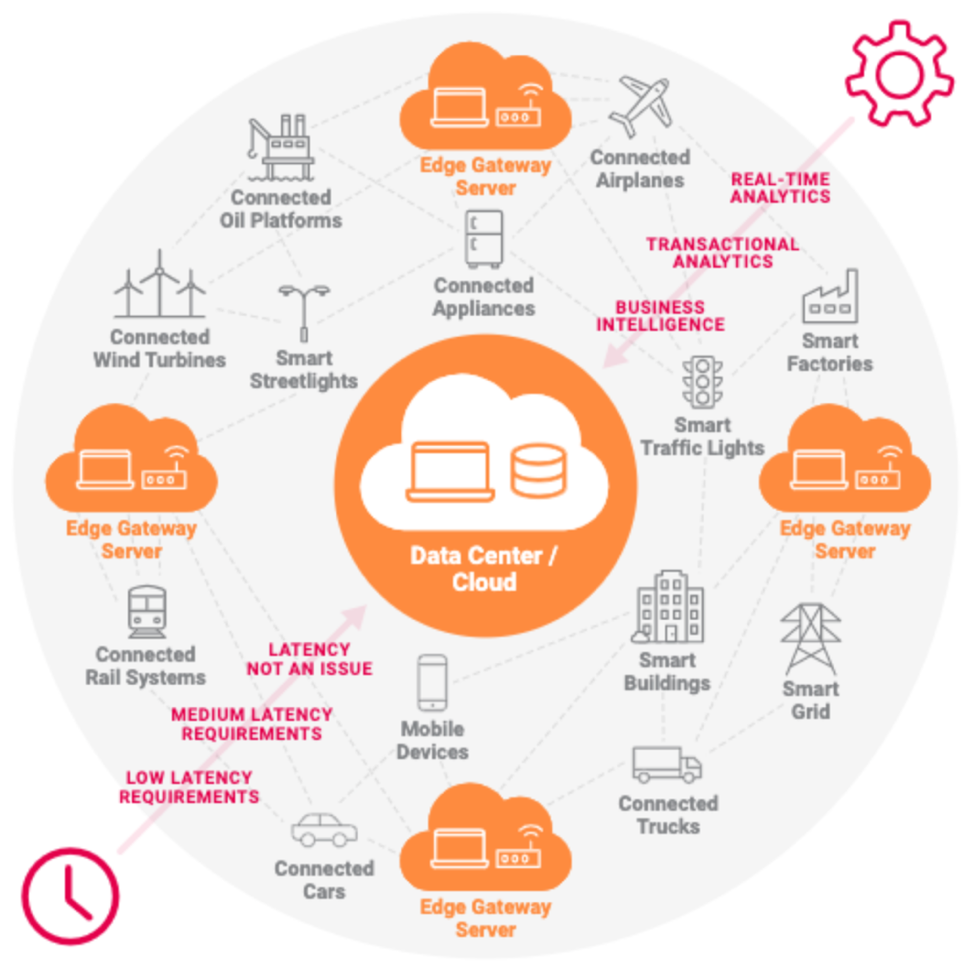
Distributed computing does require planning, though. Can you support that level of computing without air conditioning? Are the devices hardened for the environment they’ll be in?
One key consideration of edge computing deals more with staffing and operations than with technology. A site may have limited IT staff, perhaps even none. In that case, your edge device must be failsafe, because there’s no one to restart it.
Alan R. Earls’s Enabling IT at the Edge lays out these requirements and offers guidelines about how to make the most of edge computing. It also introduces Scale Computing’s platform to support edge computing.
Inside the Guide
Gorilla Guides make learning and discovery approachable and easy, and they take the guesswork out of navigating complicated IT technologies. Written by an industry expert, and brought to you by Scale Computing, this resource is packed full of trusted information about the benefits of distributing your compute power to the Edge!
Download the book and learn all about:
- Advantages of Near-Real Time Computing at the edge
- The Varieties of Edge Computing and Its Architectures
- Physical Requirements for an Edge Station
Table of Contents
Introduction: Discovering Your Edge
Chapter 1: Computing at the Edge: Keep It Simple, Do More
- Edge in Action: Edge Deployments in the Real World
- Edge Delivers
Chapter 2: The Top 5 Requirements for a Successful Edge Deployment
- A Modest Physical Footprint, with Simplified Cooling and Power
- Affordable but Effective
- Resilient and Survivable
- Simplified Resource Additions (Scale Out) and Hardware Replacement
- Repeatable, with Zero-Touch Provisioning
- A Sound Edge Approach
Chapter 3: Edge Computing, the Cloud, and You
- Likely Topologies
- Edge “Fleet Management”
- Rugged and Reliable
- Jumping to the Edge
Download Your Copy!
About the Author
Alan Earls is a Boston-area writer with extensive experience covering information technology — from its pioneering figures to today’s cutting edge development.
About Scale Computing
Scale Computing is a leader in edge computing, virtualization, and hyperconverged solutions. Using patented HyperCoreTM technology, the company’s HC3 self-healing platform automatically identifies, mitigates, and corrects infrastructure problems in real-time, enabling applications to achieve maximum uptime, even when local IT resources and staff are scarce. Edge Computing is the fastest growing area of IT infrastructure, and industry analysts have named Scale Computing an outperformer and leader in the space, including being named the #1 edge computing vendor by CRN. Scale Computing’s products are sold by thousands of value-added resellers, integrators, and service providers worldwide. When ease-of-use, high availability, and TCO matter, Scale Computing HC3 is the ideal infrastructure platform. Read what our customers have to say on Gartner Peer Insights, Spiceworks, TechValidate and TrustRadius.
Download the book here.