The 5 Pillars of Infrastructure Management
If you’ve spent any time managing IT infrastructure, you’ve experienced pain; there’s no way around that. That experience is one of the reasons that so many organizations have moved to HCI, which streamlines the management process to a great degree. Admins have learned that it’s much easier and simpler to manage HCI than what they were used to.
To understand how much simpler, it’s first necessary to grasp the 5 pillars of infrastructure management, and how virtualization—the foundation of all HCI—addresses these pillars and the various layers of data center infrastructure.
The 5 Pillars of Infrastructure Management
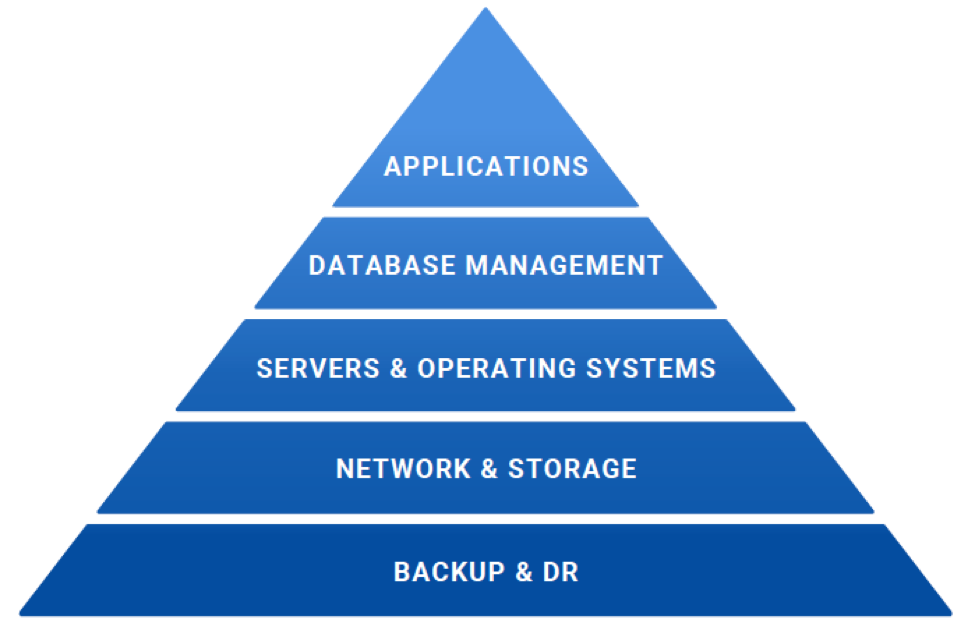
Infrastructure management is the planning, design, delivery and control of the foundational back-end support structure for applications and data. There are five major pillars of management, as shown in Figure 1:
- Applications
- Database management
- Servers and operating systems
- Network and storage
- Backup and disaster recovery
 Infrastructure management includes its own set of software for simplification and automation of day-to-day tasks and workflows, including monitoring, lifecycle management (software upgrades and the like), capacity planning, and configuration management. It focuses on the qualitative aspects of availability, scalability, security, performance, recoverability, and manageability.
Infrastructure management includes its own set of software for simplification and automation of day-to-day tasks and workflows, including monitoring, lifecycle management (software upgrades and the like), capacity planning, and configuration management. It focuses on the qualitative aspects of availability, scalability, security, performance, recoverability, and manageability.
Data Center Infrastructure Layers
A modern-day virtualization infrastructure includes a number of components, split up into a number of layers:
The Hardware Layer
The hardware layer consists of compute, storage, and networking. Depending on the type of infrastructure, these can be separate silos of hardware entities or converged into simpler appliances that combine them in different ways. Newer infrastructure architectures push some of the storage and networking logic into decoupled software layers to provide new levels of flexibility and to reduce complexity and cost.
The Infrastructure Software Layer
The infrastructure software layer is the software foundation of the data center. Software components include the hypervisor for running VMs, storage software, and networking software. These three categories consume and abstract the physical resources efficiently to create and run VMs and containers.
Additional infrastructure management software adds capabilities for automation, easy consumption of applications from a catalog, file serving, networking, security features, and hardware and software lifecycle management.
This infrastructure management is the go-to place to perform operational tasks, like creating a new VM or managing the storage infrastructure, as well as seeing operational telemetry and fixing issues. While many different infrastructure management platforms have similar features, their usability and simplicity differ significantly.
Traditional platforms require you to integrate existing—often open source—products into a coherent management platform, while others eliminate that complexity in favor of a seamless, highly integrated platform. Hyperconverged infrastructure does not only collapse the physical layers of compute, storage and networking, but it also eliminates the need for separate management solutions, each needing separate licensing, deployment and operations.
The Application Layer
Different applications need different kinds of middleware—like databases, web servers and application servers—in order to function. Depending on the application’s architecture, these all run inside a single VM, a group of VMs or in multiple containers.
Older infrastructure solutions do not usually include solutions for easy consumption of operating systems, middleware, and applications. HCI not only saves IT ops teams time by eliminating the daunting task of infrastructure deployment, it also extends the turnkey element to the application layer by providing easy consumption of operating systems, middleware, and applications through app store-like features.